In a world racing toward clean and sustainable energy solutions, nuclear power remains one of the most talked-about and misunderstood energy sources. From powering homes to debates about safety and waste, nuclear energy has reshaped the way nations think about electricity. But what exactly is nuclear energy, and how does it work?
Understanding Nuclear Energy
What Is Nuclear Energy?
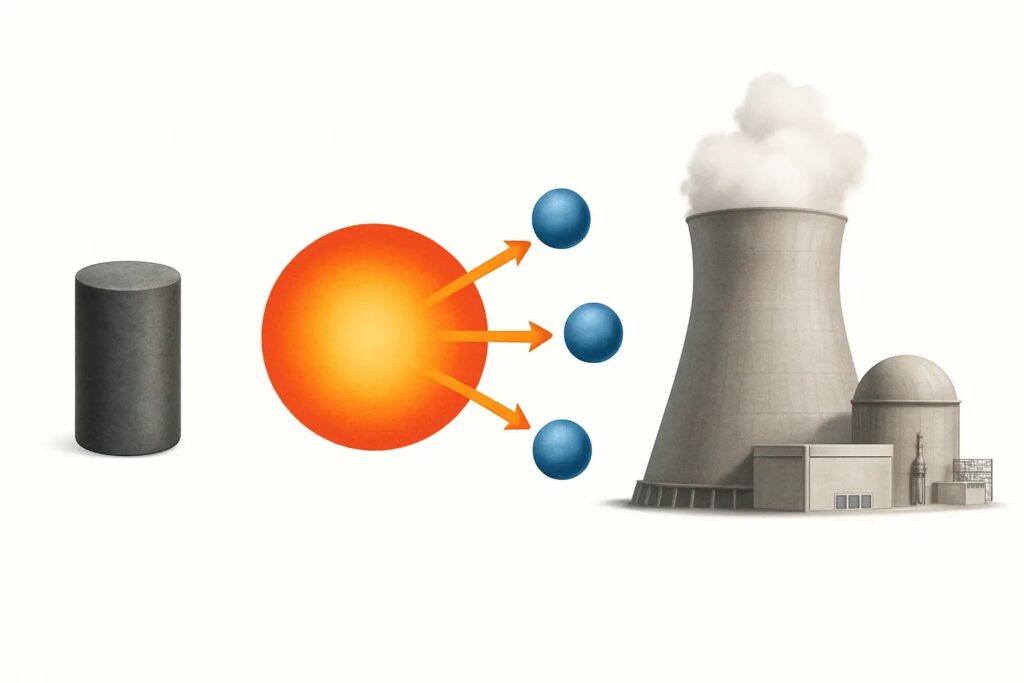
Nuclear energy is the power that comes from the nucleus—the core—of atoms. When atoms split apart or fuse together, they release enormous amounts of energy. This process is called nuclear fission (splitting atoms) or nuclear fusion (combining atoms), and it can be harnessed to generate electricity.
The Science Behind It
Fission – The Power of Splitting Atoms
Most nuclear energy used today comes from fission. Here’s how it works:
Atoms of uranium-235 or plutonium-239 are split. This splitting releases a huge amount of heat. The heat turns water into steam. Steam spins turbines. Turbines generate electricity.
This process happens inside a nuclear reactor, usually located within a power plant.
Inside a Nuclear Reactor
A nuclear reactor is a highly controlled environment designed to initiate and sustain fission. The main parts include:
Fuel rods containing uranium. Control rods to absorb neutrons and slow the reaction. Coolant, often water, that carries away the heat. Containment structure to keep radiation from escaping.
Why Use Nuclear Power?
The Pros of Nuclear Energy
Low Carbon Emissions: Nuclear plants don’t release carbon dioxide during operation. High Energy Output: A small amount of fuel generates a large amount of power. Reliable Supply: Unlike wind or solar, nuclear can operate 24/7.
The Challenges
Radioactive Waste: Spent nuclear fuel remains dangerous for thousands of years. Nuclear Accidents: Disasters like Chernobyl and Fukushima raise major safety concerns. High Costs: Building and maintaining reactors is expensive and time-consuming.
Is Nuclear Energy Safe?
Nuclear energy is one of the most regulated industries in the world. Newer reactor designs include multiple layers of safety features. However, the potential for catastrophic accidents, although rare, still exists—and this shapes public opinion heavily.
Nuclear vs. Renewable Energy
Some experts argue that nuclear is essential to reach global carbon goals. Others say investing in solar, wind, and hydro is a safer bet. Unlike renewables, nuclear doesn’t rely on weather. But unlike nuclear, renewables don’t leave behind radioactive waste.
The Future of Nuclear Energy
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
One of the most promising advancements is SMRs—compact nuclear plants designed to be safer, cheaper, and quicker to build.
Nuclear Fusion
While current nuclear power uses fission, fusion—the process that powers the sun—could someday offer limitless energy with no waste. Research is ongoing, but we’re likely decades away from seeing fusion power plants.
Conclusion: A Double-Edged Sword
Nuclear energy remains a powerful yet controversial solution to global energy needs. It offers clean, reliable power but comes with serious risks and challenges. Whether it becomes a core part of the world’s energy future depends on advances in technology, public trust, and global cooperation.