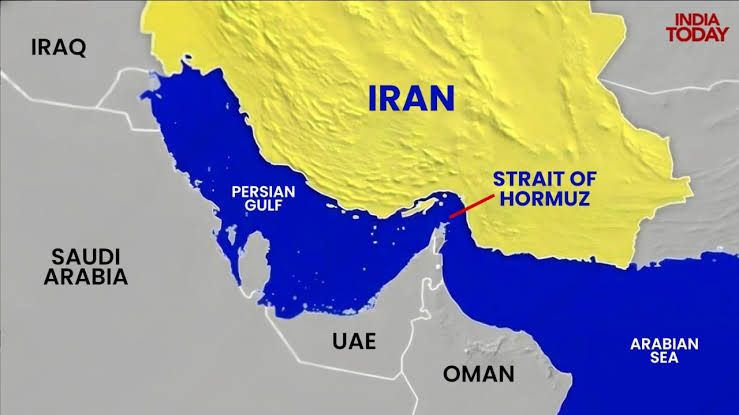
As geopolitical tensions escalate in the Middle East following recent U.S.-led airstrikes on Iran, the world’s attention has turned once again to one of the most critical maritime passageways — the Strait of Hormuz. This narrow waterway, barely 33 kilometers wide at its narrowest point, holds the potential to disrupt the global economy if tensions spiral further out of control.
What is the Strait of Hormuz?
The Strait of Hormuz is a strategically vital maritime corridor located between Iran to the north and the United Arab Emirates and Oman to the south. It connects the Persian Gulf with the Gulf of Oman and ultimately the Arabian Sea, serving as the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean.
It is considered one of the most important oil transit chokepoints in the world.
Why is the Strait of Hormuz So Important?
- About 20% of the world’s oil — roughly 17 million barrels per day — passes through this strait.
- It is the primary export route for oil-rich nations like Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Kuwait, the UAE, and Qatar.
- Liquefied natural gas (LNG) from Qatar, one of the world’s largest exporters, also transits this waterway.
Any disruption to traffic through the Strait of Hormuz can have immediate and severe consequences for the global energy market and, by extension, the global economy.
Recent Developments: Iran Threatens Closure
In response to recent U.S. airstrikes on Iranian infrastructure and the increasing naval presence of American forces in the Gulf, Iran has once again hinted at the possibility of closing the Strait of Hormuz.
Iran’s Revolutionary Guard has declared that “if Iran’s sovereignty is threatened, the strait will become unsafe for enemies.”
Historically, Iran has used this threat as a strategic deterrent, but given the rising stakes in the current crisis, experts warn that the threat may carry more weight than ever before.
What Would Happen if the Strait is Closed?
1. Oil Prices Would Skyrocket
- Analysts predict that a closure could push oil prices beyond $200 per barrel.
- Countries like China, India, Japan, and European nations, which rely heavily on Gulf oil, would suffer immediate energy shocks.
- Inflation could rise rapidly worldwide due to increased fuel and transportation costs.
2. Global Inflation and Recession Risks
- High energy costs would trigger widespread inflation, affecting food, manufacturing, transport, and power.
- Developing economies with limited oil reserves or subsidies would face budget deficits.
- The world could inch closer to recession, similar to the oil crises of the 1970s.
3. Stock Market Volatility
- The uncertainty would send global stock markets tumbling.
- Energy stocks may rise, but broader markets, particularly in Asia and Europe, would see severe losses.
4. Shipping and Insurance Chaos
- Tankers and commercial ships would reroute, facing longer travel times and higher costs.
- Maritime insurance premiums would soar due to high-risk classification of the region.
- Global supply chains could be disrupted, affecting everything from electronics to agriculture.
Military and Diplomatic Response
If Iran attempts a blockade, the U.S. Navy and its allies would likely respond militarily to secure the passage. This could escalate into a broader regional conflict involving Gulf Arab states, Israel, and potentially NATO.
The United Nations Security Council may also intervene diplomatically, though with the global power divide (Russia and China vs. the West), consensus may be hard to achieve.
China and Russia’s Position
While not openly endorsing Iran’s stance, China and Russia have expressed criticism of Western interventions and have conducted joint naval drills with Iran in recent years.
Their potential support — whether direct or strategic — could embolden Tehran and complicate any U.S.-led response.
Conclusion: A Global Flashpoint to Watch
The Strait of Hormuz remains the world’s most sensitive energy artery. In a time when global economies are already reeling from post-COVID inflation, war in Ukraine, and fragile supply chains, any disruption here could act as a global economic trigger.
The world watches anxiously. A single military miscalculation or political provocation in this narrow waterway could ignite consequences far beyond the Gulf — destabilizing markets, raising consumer prices, and endangering global peace.